Top 10 Hacker Groups of Recent Times

Hacker groups are great examples of strength in numbers. There are several groups around the world today. They have come a long way since the first reports of their activities. What started as a simple fascination with the inner workings of computer systems has evolved into coordinated attacks to steal information for various purposes.
Hacker groups cause severe financial implications for individuals and organizations. For example, the average cost of a data breach was over $3.5 million in 2020, and the figure continues to rise.
There are both young and older hackers around the world with different attack styles and motivations. Between 2017 and 2018, the number of daily web attacks blocked globally increased by 56.1%.
This article will look at the top 10 hacking groups worldwide and discuss other valuable details, such as the different types of hacker groups.
Types of Hacker Groups
As it is with individual hackers, different groups work in various capacities, with other goals. Below, we look at the three main types of hacker groups.
State-Sponsored Groups
Politics and security are two things that every nation in the world takes seriously, and they all try to get the upper hand over their adversaries. In some cases, a government employs the services of a hacker group to gain information about other countries. State or nation-sponsored hacker groups simply describe a hacker group backed by a government.
These groups use their expertise to gain confidential information about different aspects of other countries, including military plans, industrial information, and other types of data that can give their country leverage. An example of the activities of a state-sponsored hacker group is the Stuxnet attack on Iran’s nuclear plants.
Hacktivist Groups
Activists that are hacking experts create hacktivist groups. These groups usually target governments or large corporations to expose irregularities or wrongdoings. Hacktivist groups use the information obtained from the breached systems for political or social activism. However, 70% of cyberattacks are financially motivated.
Whistleblower Groups
Whistleblower groups are very similar to hacktivist groups because they also expose confidential information. These groups’ motivation includes personal grievances with an organization or discovering illegal practices within their ranks.
Top 10 Hacker Groups in Recent Years
There are many known hacker groups across the world today, with several others operating carefully under the radar. However, quite a number of them have become infamous for their high-profile attacks over the years. These groups include:
1. Tailored Access Operations
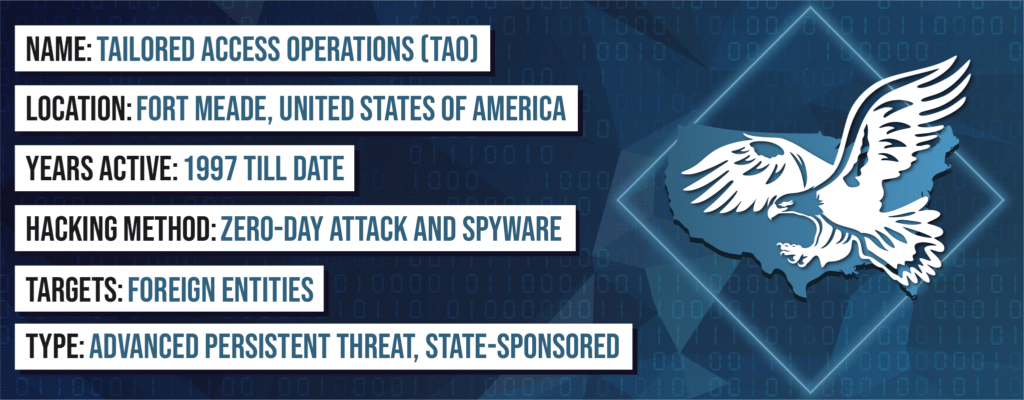
Tailored Access Operations (TAO) is one of the most sophisticated and well-equipped hacking groups. TAO is likely a state-sponsored group because reports claim they are a National Security Agency (NSA) unit. No one knows for sure how long TAO has been operating, and they would have remained in the shadows if whistleblower Edward Snowden had not exposed their existence.
Thanks to their expertise, TAO has collected almost all types of American telephone data they could get their hands on.
TAO has branches in Georgia, Denver, Texas, and Hawaii. However, there may also be other branches that the public isn’t aware of. There’s also no telling how many hackers are in this group, but so far, about 600 of them work in the NSA’s main complex in Fort Meade, Maryland.
This group has incredible unique capabilities that make it very effective. One example is QUANTUMSQUIRREL, which gives them the ability to be anyone on the internet. Additionally, they have breached computer systems through physical access or with the help of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and hardware companies. Furthermore, TAO takes advantage of loopholes that they force companies to place in their systems.
TAO also has Android and iOS software called WARRIOR PRIDE. This tool allows them to turn on phones remotely, activate their microphones, and use geolocation for tracking. Additionally, the software has tamper-proof and stealth programming.
2. Elderwood Group

Elderwood group is a general name for several other Chinese-based hacker groups such as Hidden Lynx, Linfo, and Putter Panda. This group is an APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) hacker group. They are a state-sponsored group that has been active for several years, and they continue to improve their skills.
One of the most prominent attacks carried out by the Elderwood group was “Operation Aurora,” which took place in 2010. Although Google was one of the companies hacked during the coordinated cyberattacks, the full extent of the operation is shrouded in mystery. Their other targets included supply-chain companies, defense industries, and human rights organizations.
According to experts, the coordination and level of sophistication of Operation Aurora is a clear indication that the Chinese government was pulling the strings. Other exploits by the Elderwood group can make for a long list of zero-day exploits and hacks.
3. APT28

APT28, or Fancy Bear, is another notorious Russia-based APT group. The general belief is that the Russian government sponsors the group, and they attack targets based on Moscow’s directives.
APT28 attacks involve all the standard hacking techniques, and they are usually successful. The list of their targets so far is a pretty long one that includes OSCE, ministries in Georgia, the Polish government, and NATO. While most hacker groups like to take pride in their attacks, they sometimes don’t claim responsibility or blame other groups. For example, they have tried framing the Cyber Caliphate (ISIS) for some of their activities.
Many of these hacker groups operate in countries where the government doesn’t take internet laws and freedom too seriously, and there’s no extradition agreement to the U.S., so regardless of their actions, they remain far from the reach of legal action.
Furthermore, APT28 has targeted and attacked several sporting organizations, including the Swedish Sports Confederation, the International Association of Athletics Federation, and the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). The WADA cyberattack made headlines across the world. It was retaliation for Russia’s ban from the Olympic competition after the doping scandal.
4. Tarh Andishan/Ajax

In the wake of the Stuxnet attack on Iran’s nuclear power plants, the country decided to take its cybersecurity seriously and upgrade its capabilities. This security overhaul included creating an independent state-sponsored group called Tarh Andishan and hiring already existing Iranian hacktivist groups like Ajax.
So far, there haven’t been any reports of Tarh Andishan attacking foreign government agencies. Still, they have breached airport security systems to take over gate control in Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, and South Korea. The attack gave them the ability to manipulate security credentials at the airports. Also, their other targets include telecom, oil, and gas companies.
Ajax gained its reputation by defacing websites. “Operation Saffron Rose” is the group’s most prominent attack to date. During this attack, Ajax carried out advanced phishing attacks in an attempt to steal information on U.S defense industry officials.
5. Dragonfly

Dragonfly is a known APT group. The group is likely on the Russian government’s payroll. Dragonfly targets the energy industry, power grids, and other control systems in the U.S. and Europe.
This group is infamous for its APT-style of attack, which involves watering holes and spear-phishing attacks. However, just like Stuxnet, Dragonfly can hide trojans in legitimate software industries use in their control systems.
More recently, Dragonfly has been relentless in its attacks on the US energy grid, continuously attempting to gain access to critical parts of the control system. However, the US continues to improve on its security to fend off the attacks.
6. Anonymous

Anonymous is one of the most popular hacking groups in the world. Since its emergence in 2003, the group has thrived to become a force to be reckoned with. The group doesn’t have any known leadership or organization, and many experts believe that its decentralized nature is part of the reason it has survived over the years. This is because, despite government arrests of many members of Anonymous, it doesn’t seem to affect their operations.
Since its formation, Anonymous has always been inclined towards liberal hacktivism, carrying out serious and more casual hacks.
Some of their most effective campaigns include anti-child pornography, the Occupy Movement, and anti-Church of Scientology. They are a modern-day cult symbol, and their members use the iconic Guy Fawkes masks and catchy phrases.
Anonymous prides itself on its integrity and robust moral code. For example, the group scolds members who become selfish enough to start using their names for campaigns and encourages them to leave.
7. Chaos Computer Club

Chaos Computer Club (CCC) is arguably the oldest hacker group that still exists today, and it is the largest group in Europe. A group of German hackers formed the group in 1981. CCC campaigns for transparency in governments and easy access to computers and information. Unlike other groups on this list, the CCC does not wage war on governments and industries. Instead, the group focuses more on ethical hacks that expose vulnerabilities in security systems as a means of educating people about cybersecurity.
These days, most of the members of CCC are Germans. As a result, the groups tread carefully in their campaigns, and they often seek legal advice from lawyers before hacking into systems.
CCC has survived long, and a large part of the public recognizes their abilities and accepts them. In some cases, even the press has sung their praises. However, given the size of the group, not every member always sticks to the law.
The CCC became famous in the 80s after drawing the attention of the Deutsche Bundespot to loopholes in their system. At the time, Deutsche Bundespost was trying to stifle other technologically advanced firms from competing with them. The company responded to the CCC’s claim by assuring the public that their security was airtight. CCC eventually hacked their system and stole DM 134,000. However, they returned the money the next day.
8. Syrian Electronic Army

The Syrian Electronic Army (SEA) is a hacker group that sympathizes with the Syrian people. Also, the group has links with Iran and Hezbollah. Over the years, the group has been able to carry out attacks that show just how effective they are.
Their most popular attacks include defacing several major western news outlets and locating opposition rebels with malware. However, the SEA stands out because of its style and tone. For example, the group tweeted from the AP’s account that there had been explosions at the White House, and then-president Obama was injured. The tweet had a dramatic effect on the DOW Jones Index, causing a temporary fall. In addition, the group also tweeted from a BBC Weather account that “Saudi weather station is down due to head-on collision with a camel.”
9. Morpho

Morpho (also known as Wild Neutron) is a high-profile group with very deep pockets. Since 2011, they have coordinated a series of hacks on investment, tech, and pharmaceutical companies. In addition, the group steals insider information for its profit. Some of their attacks have targeted Facebook, Twitter, Apple, and Microsoft through zero-day exploits.
Morpho is a sophisticated group. Some of their activities include bitcoins to pay hosting providers, multi-staged commands, multi-platform malware, and many more. So far, the group has managed to avoid legal action by covering its tracks properly.
10. Bureau 121

North Korea is one country that’s consistently showing off its security to intimidate other countries. The North Korean government has invested in hacking, despite being secluded from the rest of the world. Defectors have reported that some of these hackers are living rich in North Korea. Also, the government chooses the best students from their “University of Automation” school to work for them.
Bureau 121 is North Korea’s leading hacking group. Given the outdated internet infrastructure in the country, the 1800+ members of the group are located around the world.
Bureau 121’s main target has always been South Korea. The group has created malicious gaming apps, destroyed banks and broadcasting companies’ databases, and even hacked the South Korean President’s website. Bureau 121 is also thought to be connected with Guardians of Peace, which hacked Sony, costing the company $15 million.
Recent Cases of Hacking
The trend of hacking has continued to rise in recent years. In 2020 alone, for example, there were more than 3000 data breaches. In addition, according to Symantec, an average of 4800 websites are compromised by form-jacking code each month. These cyberattacks exploit vulnerabilities in systems. For example, in 2018, 34% of data breaches involved internal factors, and in 2019, 36% of the external factors involved in a data breach were linked to organized crime.
To put it in context, here are a few of the most recent cases of data breaches:
1. On January 20, 2021, a hacker leaked a Pixlr database that contained 1.9 million user records. The leak revealed sensitive details such as email addresses, usernames, user’s country, hashed passwords, and other sensitive information. The hacker went on to post the information on a free online forum.
2. The largest “Compilation of Many Breaches” (COMB) occurred on February 2, 2021, when a database of over 3.2 billion unique pairs of cleartext emails and passwords (compiled from multiple breaches of Netflix, LinkedIn, Yahoo, Bitcoin, and others) were found online. It was a concise and searchable database that was posted on a popular hacking forum, giving hackers access to multiple account credentials.
3. On April 3, 2021, a Facebook database was compromised, and the personal information of 533 million users from 106 countries was published for free in a hacking forum. Data stolen includes users’ full names, phone numbers, email addresses, and other personal information. The hackers exploited a vulnerability that Facebook had fixed in 2019 to get hold of the data.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is more critical today than ever, with countless information on the Internet, because expert hacker groups make it their business to bypass security systems. Unfortunately, no one knows how many hacker groups exist across the world. Thankfully, security systems continue to upgrade as hackers improve their skills too.
Related Posts
- Jailbroken iPhones are More Likely to be Hacked
- 5 Biggest Data Breaches to Hit India in 2023
- Top 10 Hacking Methods in Recent Times
- How to Hack Bluetooth Devices: 5 Common Vulnerabilities
- Hackers Dump Stolen FIFA 21 Code Online After Failing to Obtain a Ransom
- Chinese Hackers Allegedly Take Advantage of a Microsoft Exchange Flaw To Steal Call Records
- Vulnerabilities in Home Routers: Potential Threats from Hackers
- Researchers Discover New DNS Vulnerability With Nation-State Spying Capabilities
- What Is a Zero-Day Attack and How Can You Protect Against It?
- Researchers Find Bug in CS:GO That Could Allow Hackers Hijack Your Computer